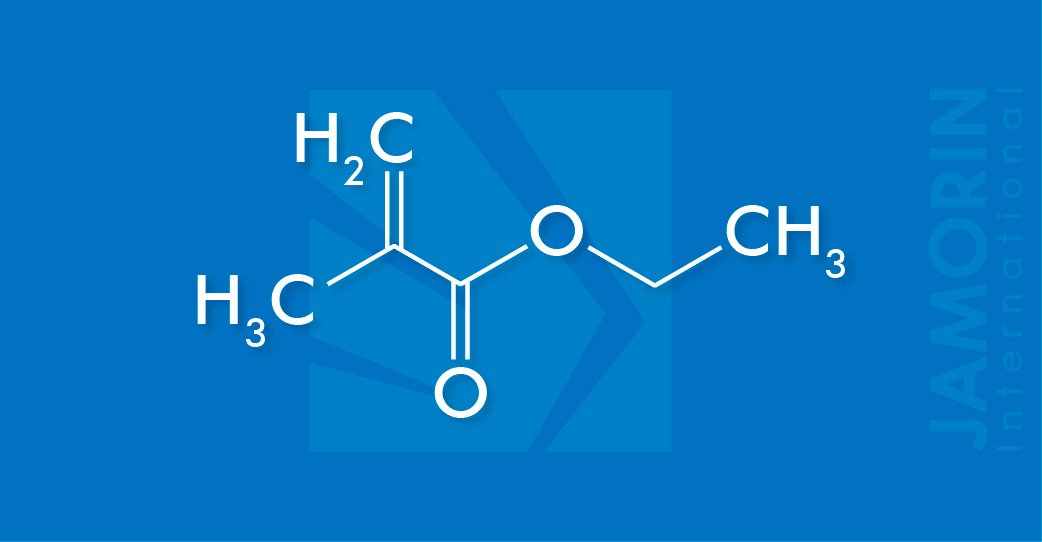
Ethyl methacrylate is the organic compound with the formula C2H5O2CC(CH3)=CH2. A colorless liquid, it is a common monomer for the preparation of acrylate polymers. It is typically polymerized under free-radical conditions.
Ethyl methacrylate was first obtained by treating ethyl 2-hydroxyisobutyrate with phosphorus pentachloride in a dehydration reaction.
Environmental issues and health hazards
The related methyl and butyl methacrylates have respective acute LD50s of 10 and 20 g/kg (oral, rat); a linear extrapolation suggests that ethyl methacrylate would have an LD50 of approximately 13 g/kg.
Acrylate esters irritate the eyes and can cause blindness.
See also
- Methyl methacrylate
- Butyl methacrylate
References